5 Amazing Ingredients of Botanical Extracts for Cosmetics Moisturizing
How Do Botanical Extracts Work in Moisturizing Cosmetics?
The moisturizing mechanism of botanical extracts varies according to the structure of their components: the water-soluble Moisturizing Components of Plant Extracts absorb and retain water mainly through the hydrogen bonding of hydroxyl or phenolic hydroxyl groups, and their different binding capacity for water affects the skin's ability to hydrate; whereas the fatty acid components of plant oils form a thin film on the skin to retain moisture and prevent drying of the skin.

For example, water-soluble components such as polysaccharides and glycosides have hydroxyl groups in their structures, which have excellent hydration properties for absorbing and retaining water through hydrogen bonding; and the phenolic hydroxyl structures in flavonoids and polyphenols also bind water through hydrogen bonding, making them also have the ability to absorb and retain water. Plant extract oils, on the other hand, retain moisture mainly by forming a thin layer of oil on the skin, preventing the skin from drying out.
In the natural world, there are 5 amazing ingredients of botanical extracts for cosmetics moisturizing, they are plant polysaccharides, plant extract oils, saponin(like triterpenoid saponins, steroidal saponins), flavonoids, and polyphenols. These botanical extract ingredients have been used for cosmetics creams, lotions, conditioners, moisturizers, beauty masks, and lip balms.
1. Polysaccharides
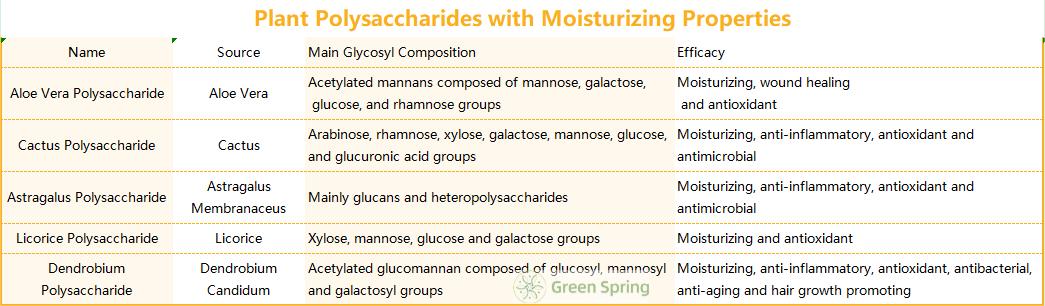
Polysaccharides are widely found in plants. The monosaccharide units in plant polysaccharides are interconnected to form a branched or linear structure, but their main chains are usually glucans, fructans, xylans, mannans or Galatians, or polymers of two or more monosaccharides. The branched structures of polysaccharides show great diversity [1]. Plant polysaccharides usually have a large number of hydroxyl groups in their structure, which have a good hydration capacity through hydrogen bonding. In addition, polar groups of plant polysaccharides such as carboxyl groups can also bind to water molecules through hydrogen bonding [2]. Therefore, most of the plant polysaccharides have the properties of hygroscopicity and water retention. Phytopolysaccharides have been widely used as humectants in various cosmetic products. The moisturizing ability of plant polysaccharides is mainly affected by the structure, composition and molecular weight of their sugar groups [3]. Many polysaccharides from plant extracts can improve skin moisturization even at low concentrations, yet reduce water loss [4].

β --glucans are a class of macromolecular cell wall polysaccharides widely found in plants and fungi, consisting of β-glycosidic bond-linked glucose groups. β -Glucan is an effective moisturizing ingredient in cosmetic formulations, which can alleviate dry skin and atopic diseases and reduce itching caused by bacterial infections, among other effects [5]. Different sources of β-glucan have different glycosidic bonds and their ratios as well as different three-dimensional structures, etc., which make β-glucan have different properties and biological activities, such as promoting wound healing, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic. Oat β-glucan is composed of glucose groups linked by β-1, 4 and 1, 3 glycosidic bonds. The mixed chain structure of oat β-glucan destroys the homogeneous structure of β-D-glucan, which makes oat β-glucan highly water-soluble and moisturizable; and high molecular weight oat β-glucan has high viscosity.

Aloe vera extract is a widely used botanical extracts for cosmetics moisturizing ingredient. Many moisturizing cosmetics contain aloe vera extract. The main active ingredient of Aloe vera extract is Aloe vera polysaccharide (Table 1), which, in addition to its excellent moisturizing effect, has a certain viscosity and gelatinous properties, and is also active in the healing of skin wounds and the repair of dry skin; furthermore, Aloe vera polysaccharides are also effective in atopic dermatitis [6]. Most of the water-soluble plant polysaccharides such as astragalus polysaccharide[7], licorice polysaccharide[8] and dendrobium polysaccharide[9] have good hydration and absorption of water properties, with good moisturizing and film-forming properties, which are effective in retaining the skin's moisture and improving the moisturization of the stratum corneum, and also all of them have efficacy such as antioxidant activity[10].
2. Plant Extract Oils
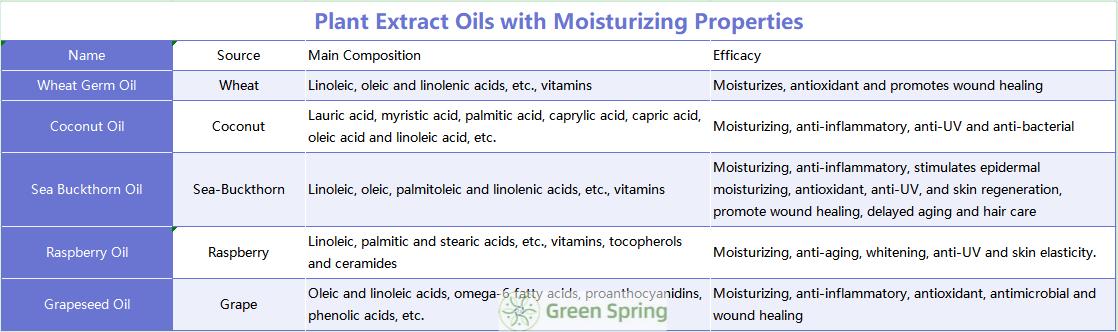
Plant extract oils form a hydrolipidic film on the surface of the skin, which not only moisturizes but also makes the skin waterproof. Plant oils strengthen the skin barrier and influence the reconstruction of the stratum corneum, preventing water loss and normalizing the sebaceous glands. Plant extract oils also have an important influence on the normal appearance and function of the skin. They are widely used in a variety of cosmetic products including creams, lotions, conditioners, moisturizers, beauty masks and lip balms [11].

Unsaturated fatty acids are the main components of plant extract oils. For example, grapeseed oil is high in omega-6 fatty acids, which regenerate the lipid barrier of the epidermis and prevent excessive water loss in dry skin and improve acne and sebaceous gland normalization in oily and seborrheic skin.
3. Saponin
Saponins are widely distributed in plants and have rich structural and functional diversity. According to different glycoside structures, saponins are categorized into triterpenoid saponins and steroidal saponins. Triterpenoid saponins are mainly found in dicotyledonous plants, while steroidal saponins are mainly found in monocotyledonous plants. Most of the saponins are a combination of hydrophobic glycosides and hydrophilic sugar groups, making the saponins highly amphoteric and possessing moisturizing, foaming and emulsifying properties [12].
The main active ingredients in Centella asiatica extracts are pentacyclic triterpenoid saponins such as hydroxy Centella asiatica glycosides. Centella asiatica extract is widely used in cosmetics for its moisturizing, wound healing, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects [13]; emulsions of Centella asiatica extract with hyaluronic acid and glycerol produce a long-lasting hydrating and moisturizing effect on the skin, while improving the skin barrier function [14].

The main active component of ginseng extract is the tetracyclic triterpenoid saponin ginsenoside. Ginsenosides not only have excellent water absorption and moisturizing effects on the skin, but also stimulate skin regeneration and wound healing by increasing the proliferation and migration of keratinocytes, repairing the skin barrier [15] [16], and have whitening and anti-wrinkle effects. In addition, the main components of many plant extracts such as Glycyrrhiza glabra [17] and Tribulus terrestris [18] are saponins. These saponin components bind to water molecules through hydrogen bonding, absorbing water and preventing water loss, which contributes to the moisturizing effect of the skin; they also repair the skin barrier as well as maintain the function of the stratum corneum and have significant anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.

4. Flavonoids
Flavonoids are usually present in multiple phenolic hydroxyl structures, and in many plants, they combine with sugar groups to form flavonoid glycosides. Flavonoid components of plants are not only hygroscopic but also have a wide variety of biological activities. The addition of flavonoids to cosmetics helps to restore elasticity and radiance to dry, sagging skin.
Quercetin is a natural extract from the flavonoid group, widely found in plants. Sophora japonica extracts containing quercetin enhance skin moisturization, repair dry, cracked and dehydrated skin, balance oil secretion, and are more effective in soothing sensitive skin. Quercetin promotes the expression of tight junction proteins in a dose-dependent manner, which enhances the tight capacity of cellular junctions, maintains the integrity of the skin barrier and regulates the dynamic balance of water, prevents skin dehydration, and reduces the sensitivity of the skin [19]; and quercetin complexed with essential oils produces a synergistic effect, which promotes moisturizing effects on the skin [20]. Quercetin also possesses antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and anti-aging properties. The combined antioxidant/anti-inflammatory effect of quercetin also favors wound healing [21].

5. Polyphenols
Polyphenols are also widely found in plants. Polyphenols have a certain moisturizing effect because they contain hydrophilic phenolic hydroxyl groups, which combine with water through hydrogen bonding to reduce water loss from the skin. The main component of tea extract is tea polyphenol, which is a typical polyphenol with a moisturizing effect. Tea polyphenols not only have the efficacy of moisturizing, sun protection, tyrosinase inhibition and anti-photo-aging [22], but also promote the differentiation of keratin-forming cells and the formation of the skin barrier, and promote wound healing [23].
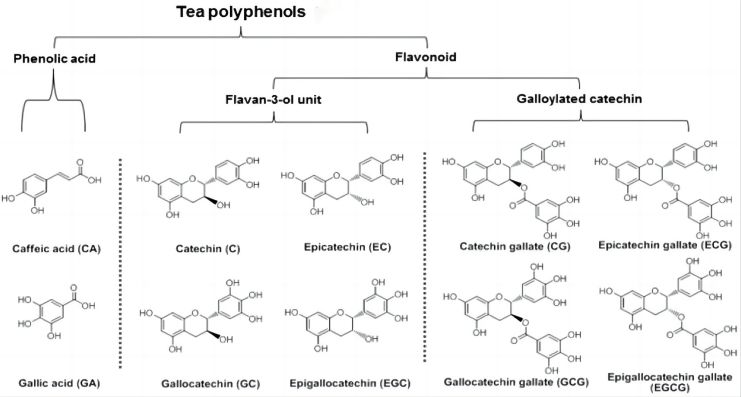
In addition, tea polyphenols also displace water-rich skin tissue fluids, reducing the viscosity of the intercellular space. Tea polyphenols have a better ability to absorb and retain moisture at relatively low humidity; i.e., when used in cosmetic formulations, they are more effective in relatively dry environments. Proanthocyanidins, on the other hand, are a class of polyphenol polymers; their phenolic hydroxyl groups are highly hydrophilic and can absorb water and maintain the water content of the stratum corneum, which results in a moisturizing effect [24]. The more phenolic hydroxyl groups in the polyphenolic structure of water-soluble polyphenolic compounds in botanical extracts, the stronger the hydration capacity and the more obvious the moisturizing effect.

Although there are plenty of advantages of botanical extracts for cosmetics as moisturizing ingredients, there are still some problems: First, except for vegetable oils, the content of ingredients with moisturizing effects in plant extracts is usually not very high; therefore, it is necessary to refine these moisturizing ingredients to improve their moisturizing effects. Secondly, there are differences in the absorption of plant extracts, especially large polysaccharides, as well as polysaccharide-based saponins and polyphenol polymers; therefore, it is necessary to use different methods or dosage forms to address their permeability and bioavailability to the skin.

Reference:
[1] Shi L. Bioactivities, isolation and purification methods of polysaccharides from natural products: a review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 92: 37-48.
[2]Jesumani V, Du H, Pei P, et al. Comparative study on skin protection activity of polyphenol-rich extract and polysaccharide-rich extract from Sargassum vachellianum[J] . PLoS ONE, 2020, 15(1): 227308.
[3]Malviya R, Srivastava P, Kulkarni G T. Applications of mucilages in drug delivery-a review[J] . Advances in Biological Research, 2011, 5(1): 1-7.
[4]Damasceno G, Silva R, Fernandes J M, et al. Use of Opuntia ficus-indica(L.)Mill extracts from Brazilian Caatinga as an alternative of natural moisturizer in cosmetic formulations[J]. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2016, 52(3): 459-470.
[5]Du B, Bian Z, Xu B. Skin health promotion effects of natural beta-glucan derived from cereals and microorganisms: a review[J] . Phytotherapy Research, 2014, 28(2): 159-166.
[6]Alvarado-Morales G, Minjares-Fuentes R, Contreras-Esquivel J C, et al. Application of thermosonication for Aloe vera(Aloe barbadensis Miller)juice processing: impact on the functional properties and the main bioactive polysaccharides[J] . Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2019, 56(2): 125-133.
[7] Salehi B, Carneiro J N P, Rocha J E, et al.Astragalus species: insights on its chemical composition toward pharmacological applications[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2020, 1-32.
[8] Rozi P, Abuduwaili A, Bao X, et al. Isolations, characterizations and bioactivities of polysaccharides from the seeds of three species Glycyrrhiza[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 145: 364-371.
[9] Guo L, Qi J, Du D, et al. Current advances of Dndrobium officinale polysaccharides in dermatology: a literature review[J] . Pharmaceutical Biology, 2020, 58(1): 664-673.
[10]Becker L C, Bergfeld W F, Belsito D V, et al. Safety assessment of Panax spp root-derived ingredients as used in cosmetics[J] . International Journal of Toxicology, 2015, 34(3): 5-42.
[11]Michalak M, Kietyka-Dadasiewicz A. Oils from fruit seeds and their dietetic and cosmetic significance[J] . Herba Polonica, 2018, 64(4): 63-70.
[12]Moses T, Papadopoulou K K, Osbourn A. Metabolic and functional diversity of saponins, biosynthetic intermediates and semi-synthetic derivatives[J] . Critical Reviews in Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 2014, 49(6): 439-462.
[13]Inamdar P K, Yeole R D, Ghogare A B, et al. Determination of biologically active constituents in Centella asiatica[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 1996, 742: 127-130.
[14]Massimo M, Adele S. The 24-hour skin hydration and barrier function effects of a hyaluronic 1%, glycerin 5%, and Centella asiatica stem cells extract moisturizing fluid: an intra-subject, randomized, assessor-blinded study[J]. Clinical Cosmetic & Investigational Dermatology, 2017, 10: 311-315.
[15]Shin K O, Choe S J, Uchida Y, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 enhances keratinocyte migration by a sphingosine-1-phosphate-dependent Mechanism[J]. Journal of Medicinal Food, 2018, 21(11): 1129- 1136.
[16] Kim E, Kim D, Yoo S, et al. The skin protective effects of compound K, a metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng[J] . Journal of Ginseng Research, 2018, 42(2): 218-224.
[17]Kayukawa C M, Oliveira M S, Kaspchak E, et al. Quillaja bark saponin effects on Kluyveromyces lactis β-galactosidase activity and structure[J]. Food Chemistry, 2020, 303: 125388.
[18]Semerdjieva I B, Zheljazkov V D. Chemical constituents, biological properties, and uses of Tribulus terrestris: a review[J] . Natural Product Communications, 2019, 14(8).
[19]Kim J, ChoN, Kim E M, et al. Cudrania tricuspidata leaf extracts and its components, chlorogenic acid, kaempferol, and quercetin, increase claudin 1 expression in human keratinocytes, enhancing intercellular tight junction capacity[J]. Applied Biological Chemistry, 2020, 63(8): 399-402.
[20]Lv X, Liu T, Ma H, et al. Preparation of essential oil-based microemulsions for improving the solubility, pH stability, photostability, and skin permeation of quercetin[J] . Aaps Pharmscitech, 2017, 18(8): 3097-3103.
[21]Karuppagounder V,ArumugamS, Thandavarayan R A, et al. Molecular targets of quercetin with anti-inflammatory properties in atopic dermatitis[J]. Drug Discovery Today, 2016, 21(4): 632-639.
[22]Wei X, Liu Y, Xiao J, et al. Protective effects of tea polysaccharides and polyphenols on skin[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(17): 7757-7762.
[23]Hsu S. Green tea and the skin[J]. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 2005, 52(6): 1049-1059.
[24]Diaconeasa Z, Stirbu I, Xiao J, et al. Anthocyanins, vibrant color pigments, and their role in skin cancer prevention[J]. Biomedicines, 2020, 8(9): 336-386.
-
Prev
Rice Bran Wax Uses: A Comprehensive Overview
-
Next
Botanical Extracts for Cosmetics Sunscreen: A Natural Way to Protect Your Skin


 English
English French
French Spanish
Spanish Russian
Russian Korean
Korean Japanese
Japanese